
Evolution from Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E to Wi-Fi 7
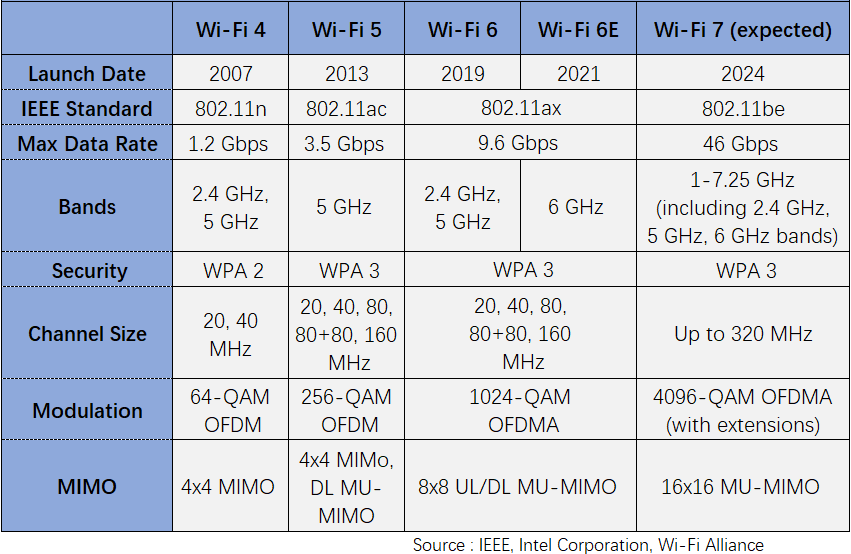
Wi-Fi 6 is the abbreviation of the IEEE 802.11ax standard. As the Wi-Fi standard evolves, the Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA) has chosen to use numerical sequencing to rename Wi-Fi for easy understanding of the type of Wi-Fi connection or support provided by devices for Wi-Fi users and manufacturers. On the other hand, the new naming method is also chosen to better highlight the significant progress of Wi-Fi technology. Wi-Fi 6 provides a lot of new features, including increased throughput and faster speed, support for more concurrent connections, etc. Currently, Wi-Fi 6 has matured and is widely used.
Wi-Fi 6E is an enhanced version of Wi-Fi 6 (E stands for Extended) that retains all the new technologies of Wi-Fi 6 and expands Wi-Fi networks from the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands to the 6GHz frequency band, ranging from 5.925GHz to 7.125GHz. This is an open new spectrum with no overlap or interference, providing a pure spectrum range. Therefore, Wi-Fi 6E has a wider bandwidth, more channels, and lower interference, which can achieve higher throughput, lower latency, and greater capacity.
Wi-Fi 7 is the next generation of Wi-Fi standard, corresponding to the new revision standard IEEE 802.11be - Extremely High Throughput (EHT). Wi-Fi 7 introduces technologies such as 320MHz bandwidth, 4096-QAM, Multi-RU, multi-link operation, enhanced MU-MIMO, and multi-AP collaboration on the basis of Wi-Fi 6, which will provide higher data transmission rates and lower latency than Wi-Fi 6. Wi-Fi 7 is expected to support throughput of up to 30Gbps, approximately three times that of Wi-Fi 6.
With the development of WLAN technology, Wi-Fi has become the primary means of accessing networks for households, enterprises, etc. New applications that have emerged in recent years have higher requirements for throughput and latency, such as 4K and 8K video (with transmission rates potentially reaching 20Gbps), VR/AR, gaming (with latency requirements less than 5ms), remote work, online video conferencing, and cloud computing. Although Wi-Fi 6 has focused on user experience in high-density scenarios, it still cannot fully meet the higher throughput and latency requirements mentioned above. The IEEE 802.11 standard organization is about to release a new revision standard, IEEE 802.11be EHT, also known as Wi-Fi 7.
According to the plan of the IEEE 802.11be EHT working group, the development of the IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) protocol is still ongoing. The entire protocol standard will be released in two Releases. Release 1 will issue Draft 1.0 at the end of 2021 and the official standard will be released at the end of 2022. Release 2 will be launched in early 2022, and the standard will be completed and released at the end of 2024.
However, although the Wi-Fi 7 wireless chip has been released, it will take some time before the final standard is set and products hit the market, expected to be around 2024. So over the next two years, Wi-Fi 6/6E will still be the dominant. Qualcomm also plans to release Wi-Fi 7 compatible products in 2023.
